Knee Ligaments: Types, Injuries & Treatment Options
The knee joint relies on its ligaments for stability and function. These tissues support the joint and help it move.
The knee has four main ligaments: the ACL, PCL, MCL, and LCL. Knowing about these is key to diagnosing and treating injuries.
This article dives deep into knee ligaments, injuries, and treatments. It explores the anatomy and function of these vital structures. This helps us understand knee health better.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the role of knee ligaments in joint stability.
- Identifying the four major ligaments associated with the knee.
- Recognizing common injuries and treatment options.
- The importance of proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Exploring the complexities of knee health and ligament function.
Understanding Knee Anatomy
Knee anatomy is a complex field that studies many parts, like ligaments. The knee joint links the lower thigh bone to the upper shin bone. It’s key for movements like walking and running.
Structure of the Knee Joint
The knee’s structure is made of bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. Bones form the base, ligaments connect bones, and tendons link muscles to bones. Cartilage reduces friction when bones move.
Role of Ligaments in Knee Stability
Ligaments are crucial for knee stability. They do several important things:
- Connect bones to each other
- Keep the knee stable during movement
- Stop the knee from moving too much
The knee joint ligaments are vital for keeping the knee stable. Damage to these ligaments can greatly affect knee function.
The Four Major Knee Ligaments
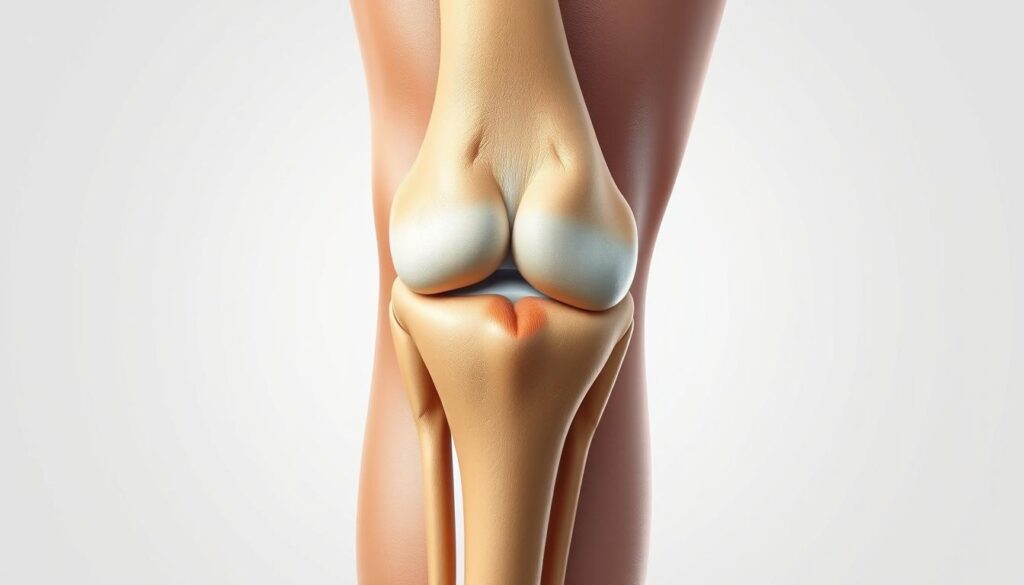
Four key ligaments surround the knee, playing a vital role in its stability and function. These ligaments are essential for maintaining knee health and enabling various physical activities.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
The ACL is a key ligament that helps stabilize the knee joint. It is located in the middle of the knee and prevents excessive forward movement of the tibia relative to the femur. ACL injuries are common, mainly among athletes involved in sports that require sudden changes in direction.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
The PCL is another crucial ligament that provides stability to the knee. It is located at the back of the knee and prevents excessive backward movement of the tibia. Injuries to the PCL often occur due to direct trauma to the front of the knee.
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
The MCL is a ligament that connects the femur and tibia on the medial (inner) aspect of the knee. It provides stability to the knee and is often injured during sports activities that involve direct blows to the knee.
Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL)
The LCL is located on the lateral (outer) aspect of the knee and connects the femur to the fibula. It works in conjunction with other ligaments to provide knee stability. Injuries to the LCL are less common compared to other knee ligaments but can still occur due to varus stress or direct trauma.
Understanding the role and function of these four major knee ligaments is crucial for diagnosing and treating knee ligament injuries effectively.
Functions of Knee Ligaments
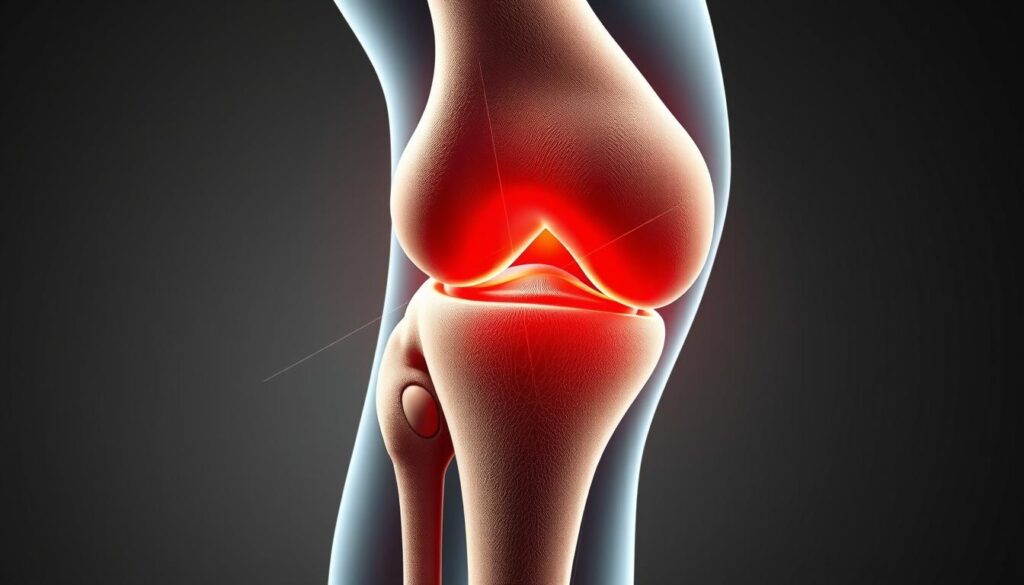
Knee ligaments are key to keeping the knee stable and moving smoothly. They help the knee work right during different activities.
Stabilization During Movement
Knee ligaments keep the knee stable by linking bones and guiding motion. This is important to avoid injuries, mainly in sports and physical activities.
Prevention of Abnormal Joint Motion
Knee ligaments stop the knee from moving too much. This helps avoid injuries or conditions that can harm the joint. As Dr. John Smith, an orthopedic specialist, says, “Ligaments are crucial in maintaining the normal trajectory of the knee joint.”
Support During Weight-Bearing Activities
Knee ligaments also support the knee when you’re walking or running. They absorb forces and spread out the weight. This is key to keeping the knee healthy and preventing osteoarthritis.
To sum up, knee ligaments are essential for knee stability, stopping abnormal motion, and supporting during activities. They play a big role in keeping the knee healthy.
Common Knee Ligament Injuries
It’s important to know about knee ligament injuries. They happen a lot in sports and everyday life. These injuries can be mild sprains or serious tears, affecting how well the knee works.
Sprains and Tears: Classification
Knee ligament injuries are graded by how bad they are. Sprains can be mild, moderate, or severe. Tears mean the ligament has broken, either fully or partially.
| Grade | Severity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mild | Minimal ligament damage, stable knee |
| 2 | Moderate | Partial ligament tear, some instability |
| 3 | Severe | Complete ligament tear, significant instability |
Mechanisms of Injury
Knee ligament injuries often happen from sudden stops or direct hits to the knee. They can also occur from bad landings after jumping. These injuries usually happen when too much force is applied to the ligaments.
High-Risk Activities and Sports
Some sports and activities are riskier for knee ligament injuries. These include sports like soccer, basketball, and football. These sports involve quick changes, jumping, and hitting, which can stress the ligaments.
Signs and Symptoms of Ligament Damage
The symptoms of knee ligament injuries vary by how severe they are. You might feel pain, swelling, instability, or have trouble walking on the affected knee.
It’s key to spot the signs and symptoms early for the best treatment. Knowing about knee ligament injuries helps prevent them and get the right medical help when needed.
Diagnosis of Knee Ligament Injuries
Diagnosing knee ligament injuries needs a detailed approach. This includes clinical exams and advanced imaging. Getting the diagnosis right is key for the right treatment.
Clinical Examination Techniques
Clinical exams are the first step. They check the knee’s stability, look for pain, and test the range of motion. A good exam can show how bad the injury is.
Imaging Modalities
Imaging is vital to confirm the diagnosis. The right imaging depends on the injury and its severity.
Evaluation
MRI is great for finding ligament injuries, like ACL and PCL tears. It shows soft tissue details well.
Ultrasound Assessment
Ultrasound is good for checking superficial ligaments, like the MCL and LCL. It’s also good for moving assessments.
X-ray and CT Scan Applications
X-rays mainly check for bone fractures. CT scans give detailed bone images and find fractures or avulsion injuries with ligament tears.
| Imaging Modality | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| MRI | High sensitivity for soft tissue injuries | High cost, limited availability |
| Ultrasound | Dynamic assessment, low cost | Operator-dependent, limited depth penetration |
| X-ray/CT | Bone structure assessment | Limited soft tissue evaluation |
Treatment Options for Knee Ligament Injuries
Knee ligament injuries need a treatment plan that fits each person. This can be conservative management or surgical interventions. The right choice depends on the injury’s severity, the patient’s health, and their lifestyle.
Conservative Management
For mild knee ligament injuries, conservative management is often the first step. It aims to lessen pain, reduce swelling, improve joint stability, and help the knee function better.
RICE Protocol
The RICE protocol is key in conservative management. It stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. This method helps in the early stages to reduce pain and swelling.
Bracing and Support
Bracing and support devices add stability to the knee. They help protect the injured ligament and aid in healing.
Physical Therapy Approaches
Physical therapy is vital in recovery. It includes exercises to boost strength, flexibility, and range of motion. A physical therapist creates a program that meets the individual’s needs.
Surgical Interventions
For serious ligament injuries or when other treatments don’t work, surgical interventions might be needed. Surgery aims to improve knee stability and function.
Ligament Reconstruction Techniques
Ligament reconstruction uses grafts to fix or replace damaged ligaments. This method is often used for ACL tears.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Minimally invasive surgical techniques aim to reduce recovery time and scarring. These methods use smaller incisions and special tools.
Advanced Surgical Options in India
India is known for its advanced orthopedic surgery, including knee ligament surgery. Many hospitals and surgeons there offer the latest techniques and technologies.
A leading orthopedic surgeon says, “The success in treating knee ligament injuries depends on picking the right treatment. It’s either conservative or surgical, based on the patient’s needs.”
Rehabilitation and Recovery Process
A good rehabilitation program is key for healing from knee ligament injuries. It includes physical therapy, bracing, and slowly getting back to activities.
Post-Treatment Recovery Timeline
The time it takes to recover depends on the injury’s severity and treatment. Usually, patients need several months to follow a rehab plan. Important steps are getting the knee to move better, building muscle strength, and improving stability.
Physical Therapy Protocols
Physical therapy is vital for knee ligament recovery. It includes exercises to improve knee movement and strength. Progressive resistance and proprioceptive training are also important.
Return to Activities Guidelines
Getting back to activities should be done slowly and carefully. It’s important to follow specific guidelines, like pain levels and knee stability. A slow return to sports or hard activities helps avoid injury.
Finding Knee Ligament Specialists in Pune and Kharadi
In Pune and Kharadi, finding the right specialist is important. Look for orthopedic surgeons who specialize in knee ligament injuries. Make sure to check their credentials, patient feedback, and success stories for the best care.
- Research local orthopedic clinics
- Check for specialists in knee ligament surgery
- Read patient testimonials and reviews
Conclusion
Knowing about knee ligaments is key to managing injuries well. It helps in getting back to normal after an injury. Knee ligament rehab is important for fixing knee function and stability.
Recovery needs a full plan, from right diagnosis to good treatment and rehab. Understanding knee ligaments helps people recover better. It lets them make smart choices about their health.
If you’re in Pune or Kharadi, finding top knee ligament doctors is crucial. The right care and rehab can help you get your knee back in shape. This way, you can do your usual activities again.
Contact By Dr. Aniket Patil :
At Om Hip & Knee Speciality Orthopedic and Physiotherapy Clinic, led by Dr. Aniket Patil — a fellowship-trained orthopedic and knee specialist based in Kharadi, Pune — we provide advanced care for knee ligament injuries, reconstruction, ACL treatment and other musculoskeletal conditions. With a patient-focused approach and modern diagnostic and treatment techniques, our clinic offers personalized solutions to help improve knee stability, reduce pain, and restore mobility. We proudly serve patients not only from Pune and Pimpri-Chinchwad (PCMC), but also from surrounding regions including Hadapsar, Kharadi, Viman Nagar, Wagholi, and Nearby Areas, delivering expert orthopedic care in a comfortable and supportive environment.

 Previous Post
Previous Post